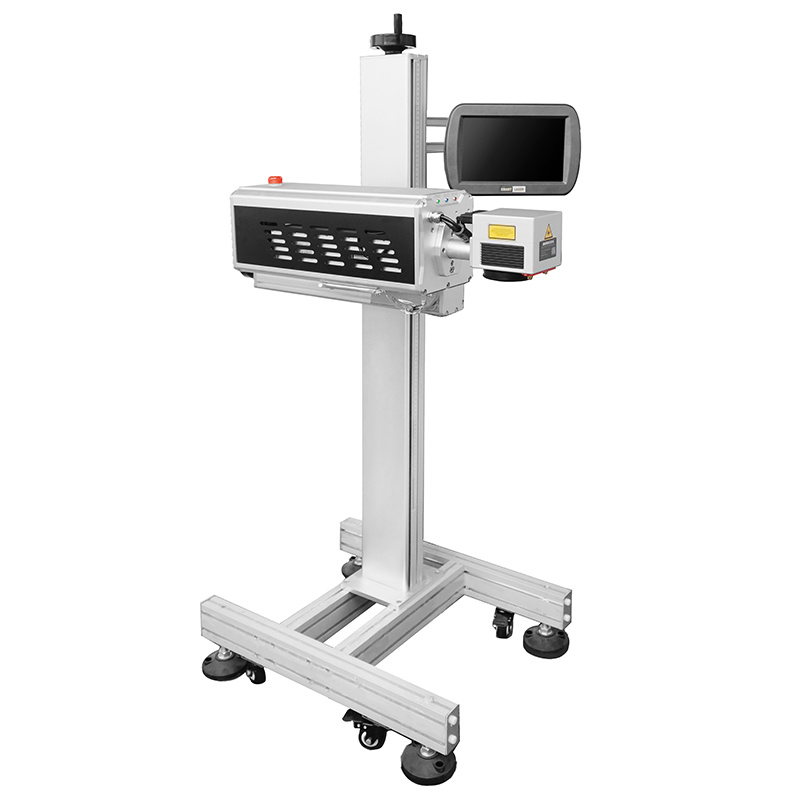
Applications
Electronic Manufacturing
Application Overview
The application solution of inkjet printers in the electronic manufacturing industry mainly revolves around core requirements such as product traceability, quality control, anti-counterfeiting, and process optimization. Combining the special characteristics of electronic components and industry standards, it provides efficient, accurate, and reliable identification solutions. The following is an overview of the plan:
Core requirements and application scenarios
1. Product identification and traceability
Application objects: PCB boards, chips, resistors, capacitors, connectors, batteries, cables, displays, and other electronic components and assemblies.
Identification content: serial number, batch number, production date, QR code, barcode LOGO、 Environmental labels (such as RoHS, WEEE), etc.
Traceability requirement: Achieve full lifecycle management from raw materials to finished products through unique identification, meeting quality management system requirements such as ISO 9001 and IATF 16949.
2. Anti counterfeiting and brand protection
Preventing counterfeit and inferior products from entering the market and safeguarding brand reputation through variable data printing, such as dynamic QR codes and encrypted information.
3. Automation and efficiency improvement
Integrate with SMT production lines, automated assembly lines, robots, etc. to achieve high-speed online coding (such as hundreds to thousands of pieces per minute), reducing manual intervention.
Selection of coding technology
Common coding techniques for electronic components with diverse materials (metal, plastic, ceramic, glass, etc.) and precision requirements include:
1. Small Character Inkjet Printer (CIJ)
Applicable scenarios: Quick identification of small electronic components (such as resistors and capacitors), supporting non-contact printing.
Advantages: Low cost, high speed, suitable for scenarios with low ink adhesion requirements.
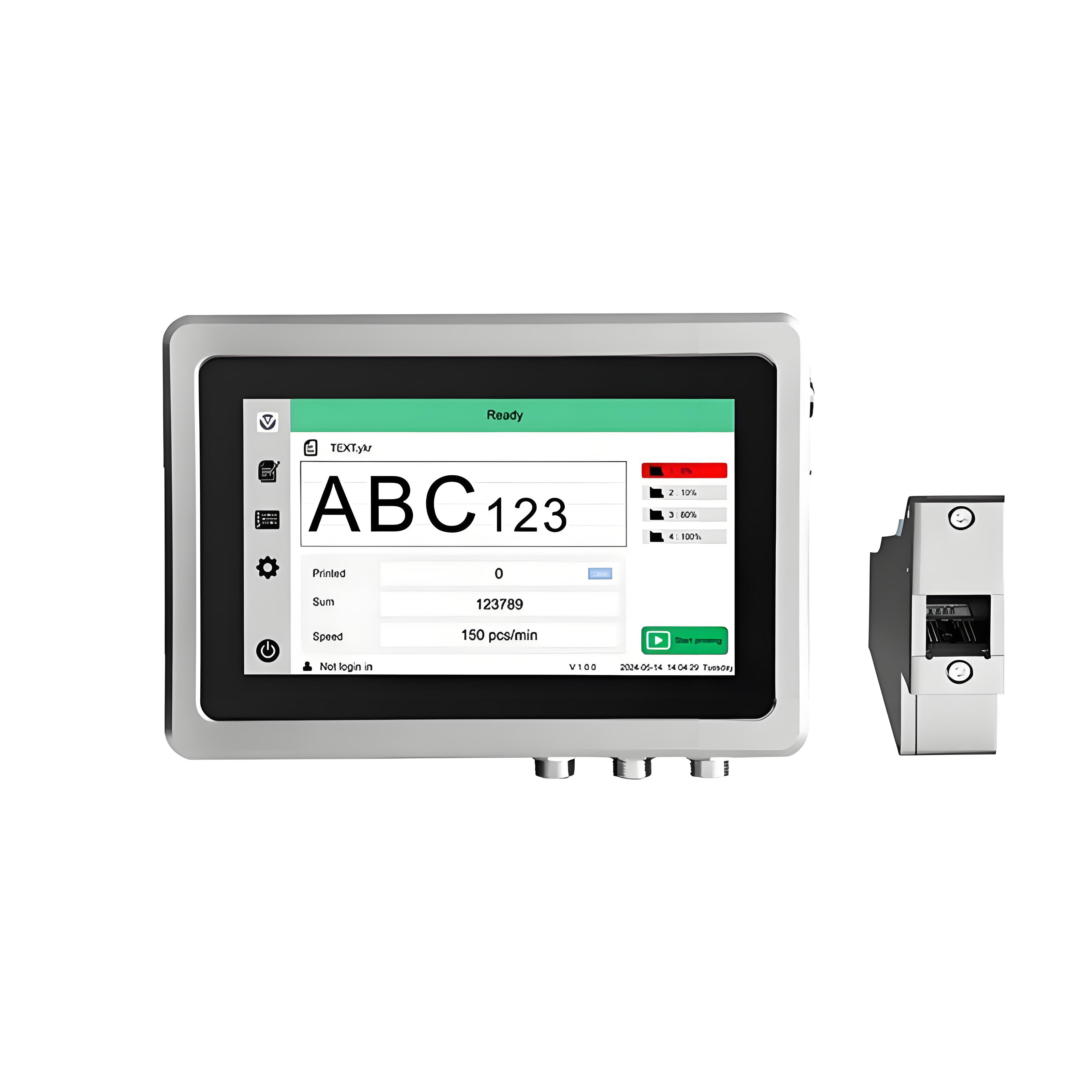
2. High resolution inkjet printer (TIJ/DOD)
Applicable scenarios: high-precision identification (such as PCB board QR codes, chip serial numbers).
Advantages: The resolution can reach over 300dpi, supporting complex graphics and small characters, and the ink dries quickly.
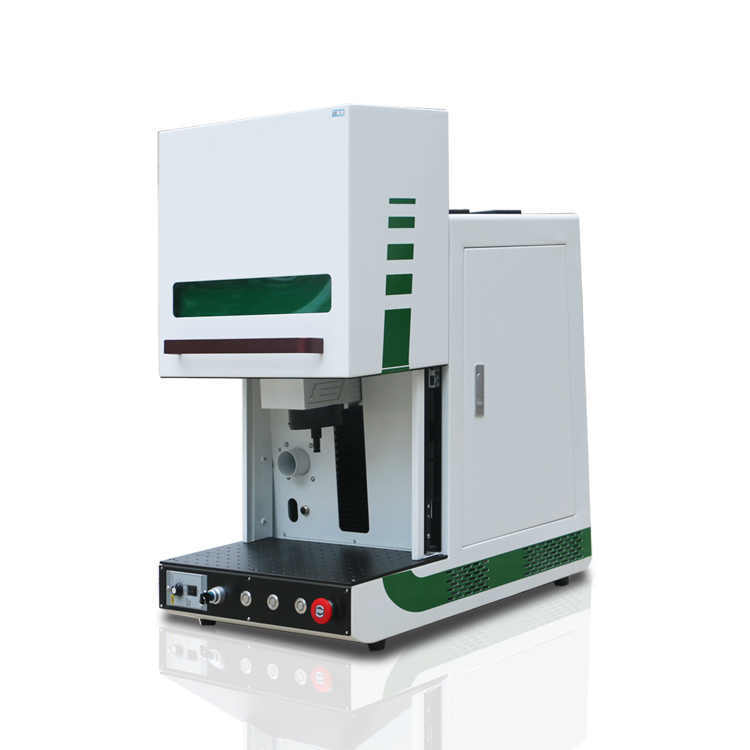
3. Laser coding machine (Fiber/CO2/UV)
Applicable scenarios: Permanent identification (such as metal shells, ceramic substrates, silicon wafers).
Advantages: No consumables, environmentally friendly, tamper proof, supporting micrometer level fine marking.
4. UV inkjet printer
Applicable scenarios: Flexible Circuit Boards (FPCs), plastic casings, etc. with high environmental requirements.
Advantages: UV ink has fast curing, no VOC emissions, and complies with RoHS standards.
Prev:
Next:
Related Cases
Silicon Transistor
Chip

Battery
Related Products