Information
VZ Growth Academy - About Optoelectronic Knowledge
05 Jun,2025
A photoelectric sensor is a type of sensor that uses light signals to detect the presence, position, color, or distance of an object. It achieves detection by emitting a beam of light and receiving changes in reflected or transmitted light, and is widely used in fields such as industrial automation, robotics, security, and consumer electronics. The following is a system introduction to photoelectric sensors:
1、 The core principle of photoelectric sensor
1. Light emission and reception
-Transmitting end: LED or laser diode is usually used to emit light beams (visible light, infrared light, etc.).
-Receiver: Receive optical signals through photosensitive components such as phototransistors and photodiodes.
-Signal processing: The optical signal at the receiving end is converted into an electrical signal, and the circuit analyzes the changes in light intensity to trigger the output signal (such as a switch signal).
2. Detection logic
-The presence of an object can block or reflect a beam of light, causing changes in the intensity of the light at the receiving end, thereby determining the position or state of the object.
2、 Types of photoelectric sensors
According to the working principle and installation method, it can be mainly divided into the following categories:
1. Through beam shooting
-Principle: The transmitting and receiving ends are separated, and objects passing through will obstruct the beam of light.
-Features: Long detection distance (up to 100 meters), strong anti-interference, but requires installation at both ends.
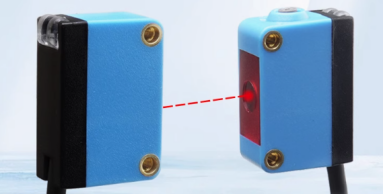
2. Retro reflective
-Principle: The transmitting end and the receiving end are integrated into the same device, and the light beam is reflected by a reflection plate. It is triggered when an object blocks the reflected light.
-Features: Easy to install, suitable for medium distance detection (several meters).

3. Diffuse reflective
-Principle: Directly detect diffuse reflected light on the surface of an object without the need for a reflector.
-Features: Single side installation, but short detection distance (several centimeters to several meters), greatly affected by object color and surface.

4. Fiber Optic
-Principle: By transmitting optical signals through optical fibers, the sensor head can be miniaturized.
-Features: Anti electromagnetic interference, high temperature/corrosion resistance, suitable for small or harsh environments.

5. Color/Mark Sensor
-Principle: Identify colors or specific markings by analyzing the wavelength or intensity of reflected light.
-Application: Printing quality inspection, label positioning.

3、 Key performance parameters
1. Detection distance: The maximum distance at which the sensor can operate stably.
2. Response time: The time from detecting an object to outputting a signal (usually in microseconds).
3. Light source types: infrared light (anti-interference), red visible light (easy to calibrate), laser (high-precision).
4. Output type: NPN/PNP switch signal.
4、 Precautions for use
1. Environmental interference
-Avoid direct exposure to strong light (such as sunlight interfering with infrared sensors), or use modulated light to resist interference.
2. Object characteristics
-Transparent/reflective objects may require filtering sensors (filtering can also be set in the coding controller).
3. Installation and calibration
-The shooting style requires strict alignment; Diffuse reflection requires consideration of the influence of background objects.
4. Maintenance
-Regularly clean the lens or fiber optic end face to prevent dust from affecting sensitivity.
5、 Common Problems and Solutions
Possible causes and solutions for the problem
Mistriggering ambient light interference to adjust sensitivity, or setting filters in the controller
Detecting unstable distance, uneven reflection on the surface of objects, and using counter reflection photoelectric technology instead
Unable to detect transparent objects with high light transmittance resulting in weak signals, using diffuse reflection optoelectronics instead
Response delay: The sensor has insufficient response time, and the response time should be selected at the μ s level
6、 Wiring Definition
Using+V, GND, and signal three wires can work, and the wiring definitions are different for each device. Please refer to the respective device manuals for details.

7、 Interpretation of NPN and PNP Concepts
NPN: represents common positive voltage, outputs negative voltage
PNP: represents common negative voltage, outputs positive voltage
NPN NO indicates that it is normally open, and when an object is detected, the black line outputs a negative voltage signal
NPN NC indicates that under normal conditions, the black line outputs a negative voltage signal. When an object is detected, the output signal is disconnected
3 PNP NO indicates that it is normally on, and when an object is detected, the black line outputs a positive voltage signal
4 PNP NC indicates that under normal conditions, the black line outputs a positive voltage signal. When an object is detected, the output signal is disconnected
8、 Separate interpretation and understanding of normally open (NO) and normally closed (NC)
The state of the taillights when sensing an object
*******************************
At this point, it can be concluded that the commonly used model in our equipment is the NPN NO photoelectric sensor.
05 Jun,2025
Classification:
Information
Latest Contents








